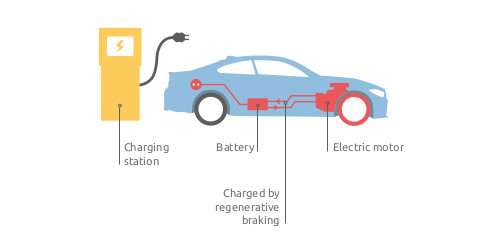
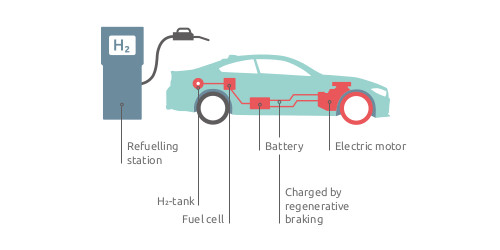
There are several ways to produce hydrogen. Depending on the type of production, the costs, the "hydrogen basis" and thus also the (positive) effects on climate change vary.
Due to its low price, the so-called steam reforming is the most common method: Hydrogen is split off from natural gas with “grey” hydrogen being the result. Advantage: low costs. Disadvantage: This process produces carbon monoxide (CO); furthermore, a fossil fuel serves as the basis for this type of hydrogen production limiting the positive impact of hydrogen.
However, efforts are being made to capture and store the carbon monoxide produced in this way. Although a fossil source still functions as raw material with this CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage) method, this production process of “blue” hydrogen is considered climate-neutral due to the lack of pollutants.
The ideal to strive towards to, however, is certainly “green” hydrogen: Energy from renewable sources (sun, wind, water) is used in electrolysis to split a water molecule into its components - namely hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2). Since this method does not produce any pollutants over the entire production chain, it is referred to as emission-free hydrogen.